By Michele Filippone - L_Sim group
In this seminar, I will discuss how quantum technologies are now able to unveil and investigate novel fundamental phenomena by simulating interacting quantum systems. In particular, we will ask: Is it possible to harness and preserve the quantum coherent properties of many-body systems?
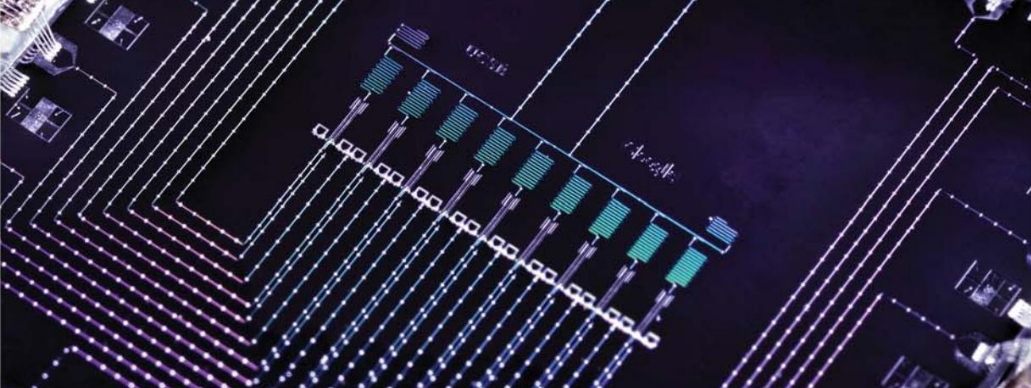
This project seems doomed to fail, as interactions in many-body systems generally lead to ergodicity, namely the inevitable loss of quantum coherence and memory about initial conditions. Nevertheless, the recent discovery of many-body localization (MBL) – a generalization of Anderson localization in the presence of interactions – has shown the possibility to circumvent ergodicity. I will illustrate an experiment in which an array of superconducting qubits probes the exotic dynamics of interacting and disordered bosons
[Ref]. Relying on real-time and interferometric probes, I will discuss how we could observe and characterize the mechanism of MBL.
[Ref] Chiaro B
et al.,
Direct measurement of non-local interactions in the many-body localized phase.
arxiv